Have you ever thought about what it would be like to have a robot that looks and moves just like a human? That is precisely what humanoid robots are all about. These advanced machines are designed to be in the shape of human beings and act like them, and this is one of the most ambitious endeavors of modern robotics. In this article, we’ll go over what humanoid robots are, how they work, their benefits, their real-world applications, and some of the most popular models being developed. Let’s get underway!
How Do Humanoid Robots Work?
Humanoid robots represent an impressive fusion of mechanical engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence. These machines are built to mimic human form and function through several key components working in harmony.
At their core, humanoid robots operate through sophisticated control systems that coordinate their movements and behaviors. These systems typically consist of a central processing unit that acts as the robot’s “brain” and translates information from various sensors into correct responses through pre-defined instructions or machine learning algorithms.
The humanoid robot’s body structure is an articulated skeleton with joints that facilitate movement as the human body moves. The joints are powered by motors or actuators that provide the necessary force to move the robot, and sensors are placed throughout the body that give feedback to the robot about its position, balance, and interaction with the environment.
Sensory systems are another crucial component, allowing humanoid robots to perceive and interact with their surroundings. These may include:
- Visual sensors (cameras) for sight
- Microphones for hearing
- Tactile sensors for touch sensitivity
- Pressure sensors for balance and grip strength
- Inertial measurement units (IMUs) for orientation
Advanced humanoid robots also incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, allowing them to adapt to new situations, learn from experience, and improve their performance over time through reinforcement learning algorithms.
What Are the Benefits of Humanoid Robots?

The human-like design of humanoid robots offers several unique advantages compared to other robotic forms. These benefits make them particularly valuable for specific applications and environments.
The most significant advantage is their ability to navigate environments designed for humans. Since our world is built to accommodate the human form—with stairs, doorways, furniture, and tools all designed for human proportions and capabilities—humanoid robots can operate in these spaces without requiring special modifications.
The familiar human-like appearance of these robots also facilitates more natural human-robot interaction. People are more comfortable conversing with robots when they look human-like, so humanoid design is instrumental in service and social purposes where the human touch is required.
Humanoid robots are also very versatile. Their movements and limbs, which mimic human motion, allow them to perform tasks from manipulation to lifting. This versatility means a single humanoid robot could replace multiple specialized robots in specific settings.
The human form also provides an excellent platform for testing and developing new robotic technologies and artificial intelligence systems. By building robots that mimic human capabilities, researchers can better understand human physiology and the challenges of creating genuinely adaptable intelligent machines.
What are the Humanoid Robot Use Cases?
The versatility of humanoid robots makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the most promising use cases:
Space Exploration
Space agencies like NASA have recognized the potential of humanoid robots for off-world exploration and maintenance. The harsh environment of space presents numerous challenges for human astronauts, from radiation exposure to the psychological effects of isolation.
Humanoid robots like NASA’s Robonaut are designed to work alongside astronauts or venture where humans cannot. These robots can perform routine maintenance tasks on spacecraft or space stations, conduct experiments, and explore planetary surfaces without requiring life support systems.
Humanoid designs are particularly valuable for space applications because they can use the same tools and interfaces designed for human astronauts. This eliminates the need to create specialized robotic tools or modify existing equipment, streamlining operations and reducing costs.
Healthcare & Medical Applications
In healthcare settings, humanoid robots show tremendous promise for patient care and medical training. Their human-like appearance and movement capabilities make them ideal for certain aspects of healthcare delivery.
Patient care applications include assisting with mobility for elderly or disabled individuals, providing medication reminders, and offering companionship to reduce isolation. Some advanced models can monitor vital signs and alert healthcare providers to potential issues.
I once visited a nursing home in California that was testing a humanoid assistant robot. What surprised me was how quickly the residents formed emotional connections with the robot. Many looked forward to their daily interactions, and the staff reported improved mood and engagement among residents who regularly spent time with the robot.
Education & Research
Education has begun to welcome humanoid robots as teachers and social learning companions. These robots can supplement classroom instruction by providing individualized attention to the students, engagingly presenting things, and even helping out in language classes.
Humanoid robots have been particularly promising for kids with special needs. Their consistency and endless patience make them valuable tools for teaching social skills to kids with autism spectrum disorders, and their attention-grabbing design serves to maintain high interest and motivation levels.
In laboratory settings, humanoid robots offer a chance to study human-robot interaction, artificial intelligence, and cognitive development. By creating robots that can learn and adapt like humans, researchers gain insights into both human cognition and the development of more sophisticated AI systems.
Educational humanoid robots also help prepare students for a future where human-robot collaboration will be increasingly common. By becoming familiar with robotic capabilities and limitations early, students develop the technological literacy needed for careers in an automated world.
Customer Service & Hospitality
The hospitality and retail sectors have begun exploring humanoid robots as customer service personnel, informants, and concierges. These machines can welcome customers, handle common queries, provide directions, and even perform basic transactions.
In hotels, humanoid robots serve as bellhops with bags, delivering room service items or providing advice on local attractions. Their human-like appearance makes them approachable to guests, while their tireless nature ensures consistent service quality regardless of the hour.
Restaurants and cafes have also begun experimenting with humanoid servers and hosts that can take orders, deliver food, and engage in simple conversation with patrons. While not yet replacing human staff entirely, these robots often serve as novel attractions that enhance the dining experience while streamlining certain aspects of service.
What are the Most Popular Humanoid Robots?
Several notable humanoid robots have captured public attention and represent the current state of the art in humanoid robotics. Here are some of the most significant examples:
Sophia by Hanson Robotics
Perhaps the most famous humanoid robot today, Sophia, was created by Hanson Robotics and first activated in 2016. What distinguishes Sophia is her remarkably human-like appearance and advanced social interaction capabilities.
Sophia features a lifelike face modeled after Audrey Hepburn. Cameras in her eyes allow for facial recognition and maintain eye contact during conversations. Her face is made from Frubber (flesh rubber), which enables her to display a wide range of facial expressions.
Beyond her appearance, Sophia is powered by sophisticated AI that allows her to engage in conversations, recognize faces, and learn from interactions. She has appeared on television shows, given interviews, and even received citizenship from Saudi Arabia (as a symbolic gesture).
While Sophia represents impressive advances in social robotics and AI, experts note that many of her capabilities remain limited compared to human intelligence. Nevertheless, she serves as an important ambassador for humanoid robotics and has helped spark public interest and discussion about AI development.
Ameca by Engineered Arts
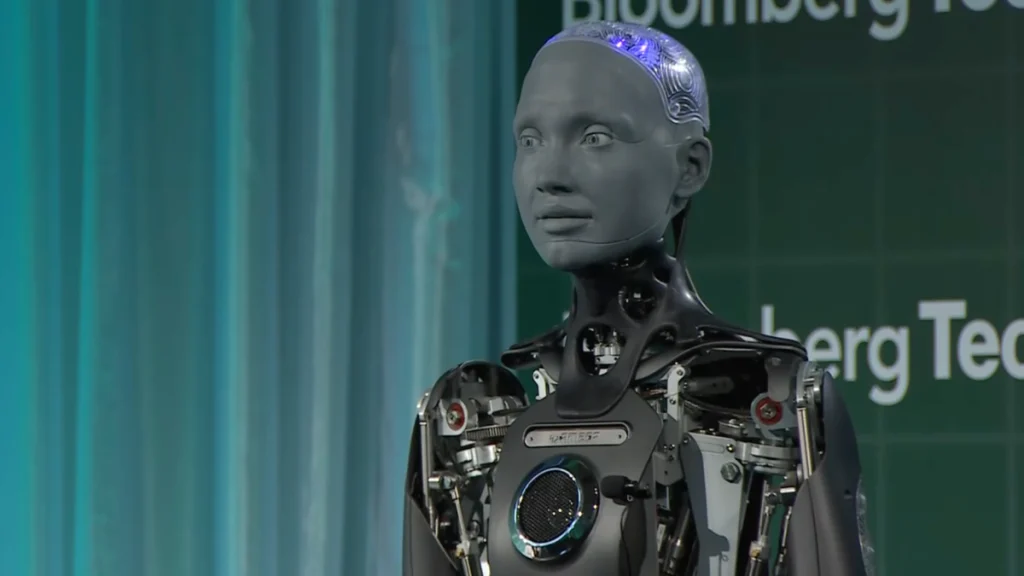
The UK-based company Engineered Arts created Ameca. It features incredibly realistic facial expressions and fluid upper body movements.
What makes Ameca particularly noteworthy is the natural quality of its facial expressions. The robot can convey surprise, confusion, contemplation, and other emotions through subtle movements that mimic human facial mechanics closely.
Unlike some humanoid robots focusing on walking or physical tasks, Ameca emphasizes human-robot interaction through natural non-verbal communication. The robot serves primarily as a platform for AI development and human-robot interaction research.
Atlas by Boston Dynamics
Atlas, developed by Boston Dynamics, represents cutting-edge, dynamic movement in humanoid robotics. At approximately 5 feet tall and weighing around 190 pounds, Atlas has demonstrated remarkable agility, balance, and adaptability.
What sets Atlas apart from many other humanoid robots is its ability to navigate challenging terrain, recover from pushes and disturbances, perform backflips and other athletic maneuvers, and adapt to unpredictable environments in real time.
The robot achieves impressive mobility through hydraulic actuation, sophisticated control algorithms, and advanced sensing. Recent versions of Atlas have demonstrated the ability to manipulate objects in their environment, expanding the robot’s potential applications.
While Boston Dynamics has primarily positioned Atlas as a research platform rather than a commercial product, the technologies developed through the Atlas program have significant implications for future humanoid robots in applications ranging from disaster response to industrial automation.
Robonaut by NASA
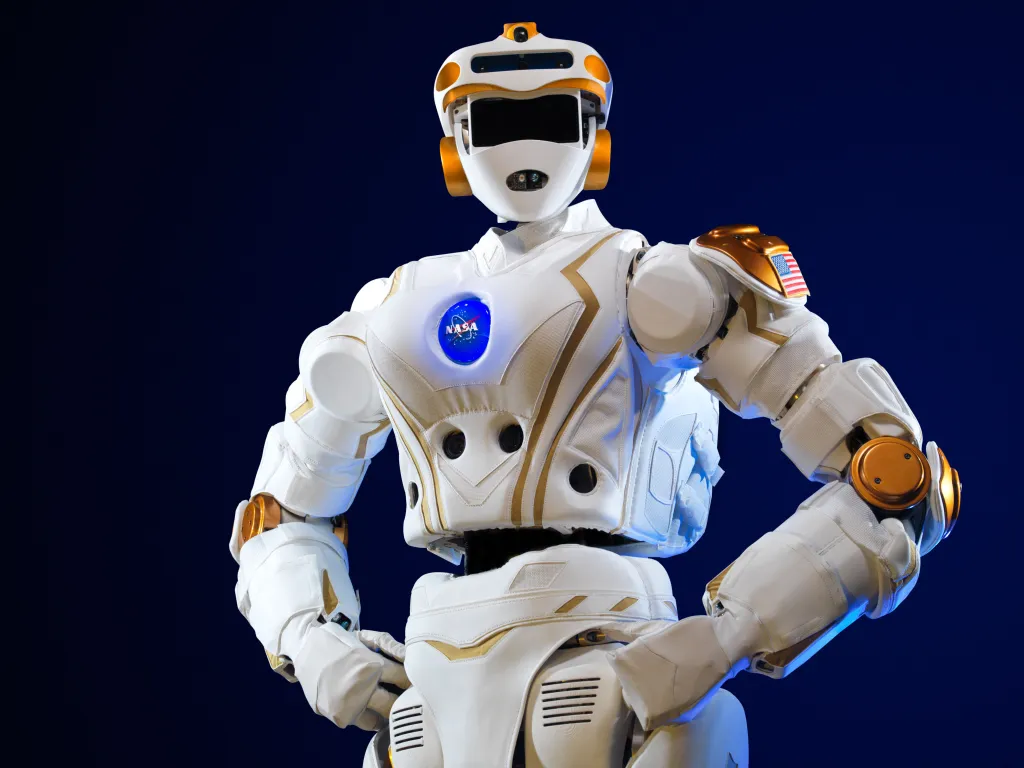

Developed from a collaborative effort by General Motors and NASA, the Robonaut is a humanoid robot designed for use in space. The latest model, Robonaut 2 (R2), was the first humanoid robot launched to the International Space Station in 2011.
The robonaut has a humanoid torso and very dexterous hands, so it can work with the same equipment used by astronauts. It can also work in human-centric environments without the need for special adaptation.
What makes Robonaut particularly valuable for space applications is its ability to perform routine, repetitive, or hazardous tasks that would otherwise require valuable astronaut time. Future versions should include legs for greater mobility around spacecraft and on planetary surfaces.
NASA continues to refine robots’ abilities, aiming to launch more advanced versions to assist in lunar and Martian expeditions. The technologies developed for Robonaut also have potential applications in fields like healthcare, manufacturing, and hazardous environments on Earth.
Conclusion
Humanoid robots are the most ambitious and fascinating area of robotics research. By mimicking human form and capabilities, these robots offer unique mobility, interaction, and adaptability features for many applications.
From space exploration and healthcare to education and customer service, humanoid robots are beginning to demonstrate their potential to transform industries and enhance human capabilities. While significant challenges remain in areas like bipedal locomotion, dexterity, and artificial intelligence, the rapid pace of advancement suggests these obstacles will continue to be overcome.
ALSO READ: Is AI-powered investing Reliable?
FAQs
A: No, humanoid robots today are not human thinkers or feelers. Although they can simulate emotions or responses through programming, they lack human consciousness and feelings. Their responses are based on algorithms and pre-programmed responses, even when using advanced AI.
A: The cost varies tremendously depending on capabilities. Research platforms like Atlas or Sophia cost millions of dollars to develop. Simpler educational humanoid robots cost $5,000-$20,000, while advanced commercial models can range from $50,000 to several hundred thousand dollars.
A: Humanoid robots are more likely to complement human workers than replace them entirely. They excel at dangerous, repetitive, or physically demanding tasks but struggle with tasks requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making. The most effective applications involve humans and robots working together.
A: Limited versions of humanoid robots are already being introduced in some settings, such as hotels, museums, and hospitals. However, widespread use in homes and offices is likely to be another 10-15 years off as issues regarding cost, reliability, and functionality are being ironed out.
A: Like any technology, humanoid robots have challenges and opportunities. To use these robots safely, physical protective features, moral programming principles, and appropriate control are required. Most contemporary humanoid robots are not powerful or fast enough to protect humans.




